In today's rapidly evolving manufacturing landscape, efficiency, precision, and adaptability are paramount. The demand for increasingly sophisticated automation solutions fuels the need for robust and customizable power transmission components. Gear motors, specifically, play a crucial role in diverse applications, from robotics and CNC machines to conveyor systems and packaging equipment. Choosing the right gear motor isn't simply about picking a component; it's about meticulously matching its power and speed ratio to the specific demands of the application – and optimizing for long-term manufacturing viability. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of selection points and calculation methods, viewed through the lens of manufacturing considerations, highlighting how MES-Drive offers innovative solutions for a future where intelligent automation is the norm.
At its core, a gear motor combines an electric motor with a gearbox to achieve the desired output speed and torque. Understanding the relationship between these parameters is fundamental. Torque (measured in Newton-meters or lb-ft) represents the rotational force, while speed (measured in Revolutions Per Minute or RPM) indicates how fast the shaft rotates. A gear motor doesn't simply multiply the motor's torque; it also reduces the speed.
The optimal matching of power and speed ratio is critical for several reasons:
Selecting the correct gear motor requires careful consideration of the following factors:

The selection process often involves iterative calculations to find the optimal gear motor. Here’s a simplified approach:
Step 1: Calculate the Required Torque (Tout):
Tout = (Moment of Inertia of Load * Angular Acceleration) + Static Torque + Friction Torque
Step 2: Determine the Motor's Required Power (Pmotor):
Pmotor= (Tout * Angular Speed) / (60 * Efficiency)
Step 3: Select the Motor Size:
Based on the calculated Pmotor and available motor ratings, choose a suitable electric motor. Consider factors like voltage, current, and power rating.
Step 4: Determine the Gear Ratio (GR):
GR = Nm/Nout = Nm/Nmotor
Where Nm is the motor’s output torque and Nout is the desired output speed. Nmotor = RPMmotor / (2π)
Step 5: Gearbox Selection: Select a gearbox with the required gear ratio to achieve the desired output speed. Consider the gearbox's efficiency and backlash. Planetary gearboxes generally offer higher torque density and efficiency compared to other types.
Example Calculation:
Let's say you need a gear motor to drive a conveyor belt with a load having a moment of inertia of 10 kg·m² and an angular acceleration of 0.5 rad/s². You want the output speed to be 100 RPM, and the conveyor belt has a static friction torque of 5 Nm and a dynamic friction torque of 1 Nm. The motor efficiency is 80%.
Tout = (10 kg·m² * 0.5 rad/s²) + 5 Nm + 1 Nm = 5 Nm + 6 Nm = 11 Nm
First, calculate the output angular speed in rad/s : 100 RPM * (2π/60) = 10.47 rad/s
Pmotor = (11 Nm * 10.47 rad/s) / (60 * 0.8) = 19.28 Watts
Now, choose a motor with a power rating of at least 20 Watts.
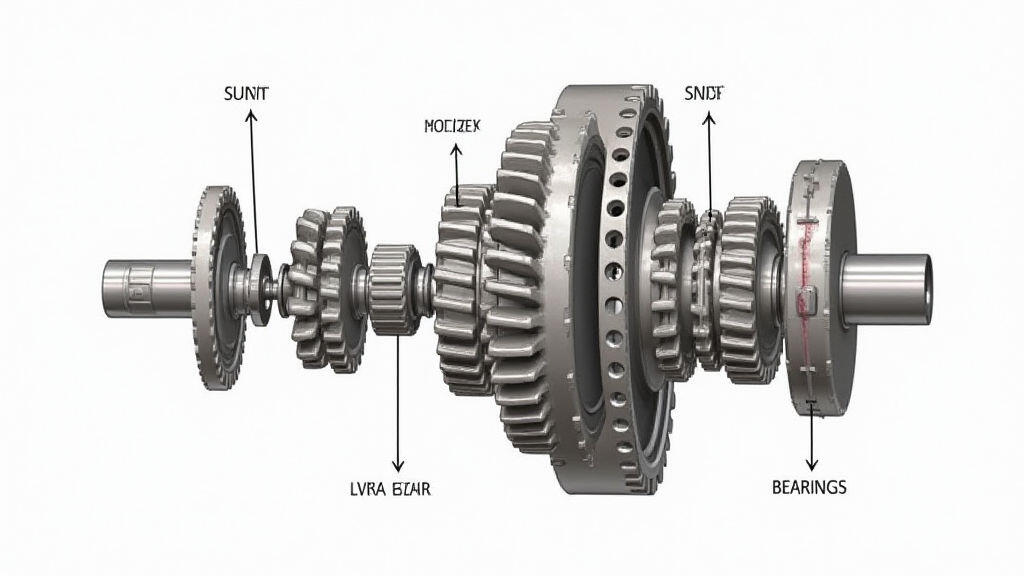
From a manufacturing perspective, the gear motor’s design should be conducive to efficient assembly, maintenance, and repair. Modular designs, simplified mounting systems, and readily available spare parts are essential.
MES-Drive is acutely aware of these manufacturing considerations. Our gear motors are designed with:
Looking Ahead: The Future of Intelligent Automation
The demand for intelligent automation is steadily increasing. Gear motors are at the heart of this trend, enabling precise control, energy efficiency, and seamless integration with other automation components. As manufacturing processes become increasingly complex, the need for highly reliable and customizable gear motor solutions will only intensify. MES-Drive is committed to driving innovation in this space, providing our customers with the power transmission solutions they need to succeed in the future of manufacturing. Our focus on robust design, efficient manufacturing, and intelligent data analytics positions us as a trusted partner for companies embracing the next wave of automation.
Leave A Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fiels are marked